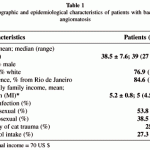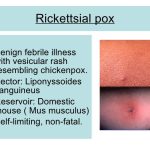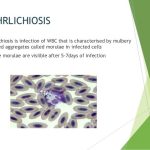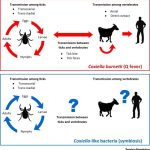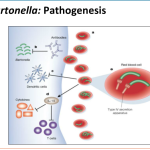
There are currently 11 known species of Bartonella, four of which are considered to be pathogenic in humans, namely B bacilliformis, B quintana, B henselae, and Bartonella elizabethae. B henselae and B elizabethae have only recently been isolated and identified, but B quintana and B bacilliformis have long been known as the causes of trench fever (B quintana) and Oroya fever and verruga peruana (B bacilliformis). The bartonellae establish intimate relationships with animal hosts, often within the vascular compartment but without causing disease. The relationship between B bacilliformis and the other three Bartonella species that are pathogenic in humans was established in the early 1990s.