Cipro (ciprofloxacin) is an antibiotic that belongs to a class of drugs called fluoroquinolones. It is used to treat a variety of bacterial infections by stopping the growth of bacteria.
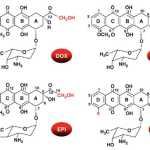
The anthracyclines are composed of a tetracyclic ring with adjacent quinone-hydroquinone moieties and a short side chain with a carbonyl group at C-13; an aminosugar is attached by a glycosidic bond to the C-7 of the tetracyclic ring. Doxorubicin (DOX) and daunorubicin (DNR) differ in the side chain terminus (-CH2OH or-CH3, respectively).
Nafcillin shares the uses of other parenteral penicillinase-resistant penicillins (e.g., oxacillin) and generally is used only in the treatment of infections caused by, or suspected of being caused by, susceptible penicillinase-producing staphylococci. For specific information on the uses of nafcillin, see Uses in the Penicillinase-Resistant Penicillins General Statement 8:12.16.12. Nafcillin sodium is administered by IM injection or by IV injection or infusion. Although nafcillin also has been administered orally, the drug is poorly absorbed from the GI tract and an oral preparation of the drug is no longer commercially available in the US.
Meropenem is a synthetic carbapenem antibiotic. Unlike imipenem, meropenem has a methyl group at position 1 of the 5-membered ring, which confers stability against hydrolysis by dehydropeptidase 1 (DHP 1) present on the brush border of proximal renal tubular cells and therefore does not require concomitant administration with a DHP-1 inhibitor such as cilastatin.

Carbacephems are b-lactam antibiotics structurally and pharmacologically related to cephalosporins; however, carbacephems contain a methylene group instead of sulfur in the dihydrothiazine ring of the cephalosporin nucleus, resulting in a tetrahydropyridine ring. This structural modification does not affect microbiologic activity, but substantially improves stability in aqueous solution and in serum, plasma, and other body fluids. Loracarbef is the carba analog of cefaclor, a second generation cephalosporin. SumMon® (see Users Guide).

Macrolides are a class of drugs that inhibit bacterial protein synthesis. They demonstrate excellent activity against atypical organisms (Mycoplasma, Chlamydia, and Legionella species), but have variable activity against typical pathogens (S. pneumoniae and H. influenzae). Macrolides are indicated for use in mild-to-moderate community-acquired pneumonia and are typically used as first- and second-line agents for this indication.
Sparfloxacin is expected to be especially useful against penicillin-resistant S. pneumoniae and multidrug-resistant H. influenzae and M. catarrhalis. Rhone-Poulenc Rorer is also studying the use of sparfloxacin for acute maxillary sinusitis, skin infection, and complicated urinary tract infection. In clinical trials, sparfloxacin (Zagam) was comparable to erythromycin and cefaclor for clearing community-acquired pneumonia.