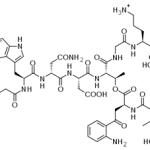
Tuberculosis, once thought to be a disease virtually eliminated in the first world has become a major health concern. Health care workers, the immunosuppressed, and HIV-positive people are particularly at risk. The rising rate of infection with M. tuberculosis along with the increase in antibiotic-resistant strains has made the development of new antibiotics for the treatment of tuberculosis of major importance for public health. Rifapentine (Priften, Hoechst Marion Roussel), a member of the rifamycin class of antibiotics, was approved in June, 1998 for the treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis.