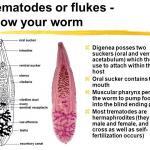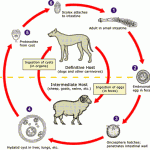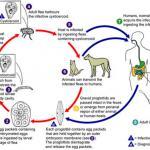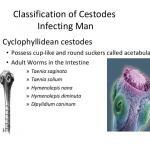
Human infections caused by cestodes, or tapeworms, may occur within the lumen of the bowel, where adult cestodes attach themselves to the host intestine (Box 1). Alternatively, human infection may be the result of dissemination of cestodes from the bowel to involve extraintestinal sites, often by larval forms of the parasite. The life cycle of cestodes is determined by definitive hosts, in whom the mature adult worm lives, and intermediate hosts, which harbor the larval forms of the parasite. Humans are a definitive host for six cestodes: Diphyllobothrium latum, Taenia solium, Taenia saginata, Hymenolepis diminuta, Hymenolepis nana, and Dipylidium caninum.