Trade Name Drug: Cubicin
Generic Name Drug: Daptomycin
Company: Cubist Pharm
Indication/Use: Skin infections
Approval Date: Sept. 12, 2000 FDA Class: 1P
Development
Hospital-acquired infections caused by gram-positive bacteria including Staphylococcus aureus, coagulase-negative staphylococci (Staphylococcus epidermidis), streptococci, and enterococci have become increasingly common and problematic because of their capacity to cause serious and life-threatening diseases in both healthy and debilitated individuals. These infections often occur as pneumonia in hospitalized patients, or as skin infections in persons with burns or wounds. Staphylococcal infections had been successfully treated with penicillin since the 1940s, but strains began showing resistance as early as the next decade.
Methicillin was developed in the 1960s specifically because of its antistaphylococcal activity, but by 1968 there were the first reported cases of methicillin-resistant staphylococci (MRSA and MRSE). By 1997, 50% of staphylococcal infections contracted by hospital patients were resistant to penicillins, compared with 2% just 25 years earlier. And similar increases have been observed among various enterococci and streptococci, especially Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Vancomycin has been used as the “last line of defense” against staphylococcal infections as well as for certain streptococcal and enterococcal infections. However, in recent years cases of vancomycin-resistant staphylococci (VRSA) and enterococci (VREF) have become more prevalent across the globe. Also, drug-resistant infections, particularly those caused by gram-positive pathogens, have spread from hospitals and nursing homes to communities.
Over the past several years a number of new antibacterials, including linezolid (Zyvox), quinupristin/dalfopristin (Synercid) and now daptomycin, have been introduced to target some of these multidrug-resistant gram-positive organisms. These new products are effective because they have novel mechanisms of action or bind in unique ways to otherwise resistant bacterial targets.
Daptomycin (see figure) is a cyclic lipopeptide antibiotic that is derived from the fermentation of Streptomyces roseosporus. Because of its unique structure, it has a mode of action distinct from any other antibacterial drug currently marketed and thus retains activity against important pathogenic gram-positive cocci, including MRSA, VRSA and VREF. Other advantages of daptomycin include once-daily dosing and a favorable side-effect profile, which facilitates drug administration and patient tolerance.
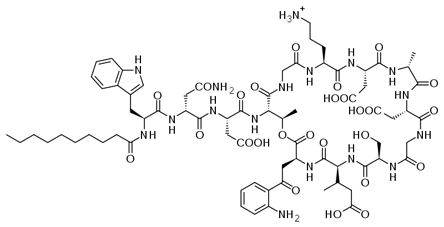
Mechanism of Action
Daptomycin (Cubicin) is a cyclic lipopeptide natural product and thus represents a new structural class of antibacterial drugs with a mechanism of action that is different from those of other available antibiotics. It produces its antimicrobial effects by binding to bacterial membranes and causing a rapid depolarization of membrane potential.
The loss of membrane potential leads to inhibition of protein, DNA, and RNA synthesis, which results in bacterial cell death. Thus daptomycin exhibits a rapid, concentration-dependent bactericidal activity against gram-positive organisms in vitro as demonstrated both by time-kill curves and by MBC/MIC ratios using broth dilution methodology. The in-vitro spectrum of daptomycin activity encompasses most clinically relevant aerobic gram-positive pathogenic bacteria.
Daptomycin (Cubicin) retains activity against antibiotic-resistant gram-positive bacteria, including isolates resistant to methicillin, vancomycin, and linezolid. In-vitro studies have demonstrated additive or indifferent interactions of daptomycin with other antibiotics. Antagonism, as determined by kill-curve studies, has not been observed. In-vitro synergistic interactions occurred with aminoglycosides and beta-lactam antibiotics against some isolates of staphylococci and enterococci, including some MRSA isolates. At present, no mechanism of resistance to daptomycin has been identified, and there are no known transferable genetic elements that confer daptomycin resistance.
Pharmacokinetics
Daptomycin (Cubicin) is administered intravenously and its pharmacokinetics are nearly linear and time-independent at doses up to 6 mg/kg administered once daily for seven days. Steady-state concentrations are achieved by the third daily dose and the apparent volume of distribution at steady state is approximately 0.09 L/kg. Daptomycin displays concentration-independent plasma protein binding (92%) and is bound primarily to serum albumin.
Protein binding does decline in patients with a creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/min (88%), including hemodialysis patients (86%) and continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) patients (84%). The extent of protein binding appears to be independent of hepatic function. Daptomycin does not appear to be a substrate for cytochrome isozymes and it is unlikely that it will inhibit or induce the metabolism of drugs metabolized by these hepatic enzymes. Inactive metabolites of daptomycin have been detected in the urine, but the site and enzymes of metabolism have not been identified.
Daptomycin (Cubicin) is excreted primarily by the kidneys with the majority of the excreted dose (52%) being the active drug. Because renal excretion is the primary route of elimination, dosage adjustment is necessary in patients with severe renal insufficiency (Ccr less than 30 mL/min) (see Dosage and Administration). No dosage adjustment is necessary for obese patients, elderly patients with normal (for age) renal function, or in patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment. The pharmacokinetics of daptomycin in patients with severe hepatic insufficiency have not been evaluated.
Cubicin (Daptomycin): Clinical Profile
Daptomycin is indicated for the treatment of complicated skin and skin structure infections caused by susceptible strains of the gram-positive microorganisms including Staphylococcus aureus (including methicillin-resistant strains), Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus dysgalactiae and Enterococcus faecalis (vancomycin-susceptible strains only).
The efficacy of daptomycin for these indications was demonstrated in two randomized, multinational, controlled trials involving 1,079 adult patients with clinically documented complicated skin and skin-structure infections. In these studies daptomycin (4 mg/kg/day IV) was compared with either vancomycin (1 g/day IV) or a penicillin (ie, nafcillin, oxacillin, cloxacillin, or flucloxacillin; 4 to 12 g/day IV). Patients with bacteremia at baseline were excluded from these studies. The efficacy end points in both studies were the clinical success rates in the intent-to-treat (ITT) population and in the clinically evaluable (CE) population.
Patients could switch to oral therapy after a minimum of four days of IV treatment if clinical improvement was demonstrated. In one of these trials (study 9801), clinical success rates in the ITT population were 62.5% (165/264) in patients treated with daptomycin compared to 60.9% (162/266) in patients treated with comparator drugs. Clinical success rates in the CE population were 76% (158/208) in patients treated with daptomycin and 76.7% (158/206) in patients treated with comparator drugs. In the trial (study 9901), clinical success rates in the ITT population were 80.4% (217/270) in patients treated with daptomycin compared to 80.5% (235/292) in patients treated with comparator drugs.
Clinical success rates in the CE population were 89.9% (214/238) in patients treated with daptomycin and 90.4% (226/250) in patients treated with comparator drugs. The emergence of daptomycin-resistant isolates in trials was rare, occurring in 2 of more than 1,000 patients treated. Combination therapy may be clinically indicated if the documented or presumed pathogens include gram-negative or anaerobic organisms. To date the safety and efficacy of daptomycin in patients younger than 18 years of age have not been established.
Adverse Reactions
Most daptomycin-associated adverse events reported in clinical trials to date were mild or moderate in severity and required drug discontinuation in less than 3% of the trial population. The most commonly reported adverse reactions occurring with an incidence of 3% to 6% included GI effects (constipation, nausea, diarrhea, vomiting), injection site reactions, rash, pruritus, headache, insomnia, and abnormal liver function tests. The incidence of these events in the daptomycin-treated patients was comparable to or lower than observed in the comparator drug treatment groups (vancomycin or penicillin).
Additional adverse events that occurred in 1% to 2% of patients in either daptomycin- or comparator-treatment groups in clinical trials included edema, cellulitis, hypoglycemia, elevated alkaline phosphatase, cough, back pain, abdominal pain, hypokalemia, hyperglycemia, decreased appetite, anxiety, chest pain, sore throat, cardiac failure, confusion, and Candida infections. Again the incidence of these adverse effects was similar in the daptomycin and comparator drug treatment populations. In some trials, elevations in serum creatine phosphokinase (CPK) were reported as clinical adverse events in a small percentage (3%) of the daptomycin-treated patients, compared with less than 2% of the comparator-treated patients. While these patients typically did not develop symptoms of myopathy (muscle pain or weakness, particularly of the distal extremities) it is recommended that patients receiving daptomycin be monitored weekly for possible symptoms of myopathy and CPK levels.
Daptomycin (Cubicin) should be discontinued in patients with unexplained signs and symptoms of myopathy in conjunction with CPK elevation greater than 1000 U/L (approximately 5 times ULN), or in patients without reported symptoms who have marked elevations in CPK (10 x ULN or greater). In addition, therapy with other drugs associated with rhabdomyolysis, such as HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, should be suspended in patients receiving daptomycin. In one trial involving the use of daptomycin in community-acquired pneumonia, the death rate and rates of serious cardiorespiratory adverse events were higher in daptomycin-treated patients than in comparator-treated patients.
However, these differences were probably caused by a lack of therapeutic effectiveness of daptomycin in the treatment of CAP in patients experiencing these adverse events. Pseudomembranous colitis, resulting from antibiotic-induced alterations of the normal flora of the colon that permit overgrowth of clostridia, has been reported with nearly all antibacterial agents, including daptomycin. Therefore, it is important to consider this diagnosis in patients who present with diarrhea subsequent to the administration of daptomycin or any antibacterial agent.
Daptomycin (Cubicin) is a pregnancy category B drug. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women and thus daptomycin should be used in pregnancy only if clearly needed. Also, since it is not known if daptomycin is excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when administering daptomycin to nursing women.
Cubicin (Daptomycin): Drug Interactions
To date relatively few drug interaction studies have been conducted with daptomycin. It has been shown that coadministration of daptomycin (6 mg/kg/day for five days) and warfarin (25 mg single oral dose) has no significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of either drug, and that international normalized ratios (INR) are not significantly altered. However, as a precaution, patients receiving warfarin should be monitored for the first several days after initiating concurrent daptomycin therapy. Also, like daptomycin (Cubicin), HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors may cause myopathy, which is manifested as muscle pain or weakness associated with elevated levels of CPK. Thus it may be prudent to temporarily suspend HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor therapy in patients receiving daptomycin.
Dosage and Administration
Daptomycin (Cubicin) is provided as a lyophilized powder for injection in 250- and 500-mg strengths. Daptomycin is compatible with 0.9% sodium chloride injection and lactated Ringer’s injection. The powder should be reconstituted with 0.9% sodium chloride injection (5 mL for 250-mg and 10 mL for 500-mg strength).
The reconstituted solution should be diluted further with 0.9% sodium chloride injection to be administered by IV infusion over a period of 30 minutes.
Daptomycin is not compatible with dextrose-containing diluents, and additives or other medications should not be added to daptomycin products or infused simultaneously through the same IV line. If the same IV line is used for sequential infusion of several different drugs, the line should be flushed with a compatible infusion solution before and after infusion with daptomycin.
For complicated skin and skin structure infections, 4 mg/kg of daptomycin should be administered over a 30-minute period by IV infusion once every 24 hours for seven to 14 days.
Based on the observation in clinical trials that creatine phosphokinase (CPK) elevations appeared to occur more often when daptomycin was dosed more frequently than once daily, this drug should not be administered more frequently than once a day. Since daptomycin (Cubicin) is eliminated primarily by the kidneys, dosage modification (4 mg/kg once every 48 hours) is recommended for patients with creatinine clearance (CrCl) less than 30 mL/min, including patients receiving hemodialysis or CAPD.
When possible, daptomycin should be administered following hemodialysis on hemodialysis days.

